1. What is C#?
C# is an object-oriented, type-safe, and managed language that is compiled by .Net framework to generate Microsoft Intermediate Language.
Type Safe: A type-safe language is one where the only operations that one can execute on data are the ones that are condoned by the data’s type. That is, if your data is of type X and X doesn’t support operation y, then the language will not allow you to to execute y(X).
2. Explain types of comment in C# with examples
Single line
Example:
//This is a single line comment
ii. Multiple line (/* */)
Example:
/*This is a multiple line comment We are in line 2 Last line of comment*/
iii. XML Comments (///).
Eg:
/// summary; /// Set error message for multilingual language. /// summary
3. Can multiple catch blocks be executed?
No, Multiple catch blocks can’t be executed. Once the proper catch code executed, the control is transferred to the finally block, and then the code that follows the finally block gets executed.
4. What is the difference between public, static, and void? what are access specifiers?
Public declared variables or methods are accessible anywhere in the application. Static declared variables or methods are globally accessible without creating an instance of the class. Static member are by default not globally accessible it depends upon the type of access modified used. The compiler stores the address of the method as the entry point and uses this information to begin execution before any objects are created. And Void is a type modifier that states that the method or variable does not return any value.
Access modifiers are keywords used to specify the declared accessibility of a member or a type. Access modifiers are keywords used to specify the scope of accessibility of a member of a type or the type itself. For example, a public class is accessible to the entire world, while an internal class may be accessible to the assembly only.
Why use access modifiers?
Access modifiers are an integral part of object-oriented programming. Access modifiers are used to implement the encapsulation of OOP. Access modifiers allow you to define who does or who doesn’t have access to certain features. In C# there are 6 different types of Access Modifiers:
| Modifier | Description |
| public | There are no restrictions on accessing public members. |
| private | Access is limited to within the class definition. This is the default access modifier type if none is formally specified |
| protected | Access is limited to within the class definition and any class that inherits from the class |
| internal | Access is limited exclusively to classes defined within the current project assembly |
| protected internal | Access is limited to the current assembly and types derived from the containing class. All members in the current project and all members in derived class can access the variables. |
| private protected | Access is limited to the containing class or types derived from the containing class within the current assembly. |
5. What is an object?
An object is an instance of a class through which we access the methods of that class. “New” keyword is used to create an object. A class that creates an object in memory will contain the information about the methods, variables, and behavior of that class.
6. Define Constructors
A constructor is a member function in a class that has the same name as its class. The constructor is automatically invoked whenever an object class is created. It constructs the values of data members while initializing the class.
7. What is Jagged Arrays?
The Array which has elements of type array is called jagged Array. The elements can be of different dimensions and sizes. We can also call jagged Array as an Array of arrays.
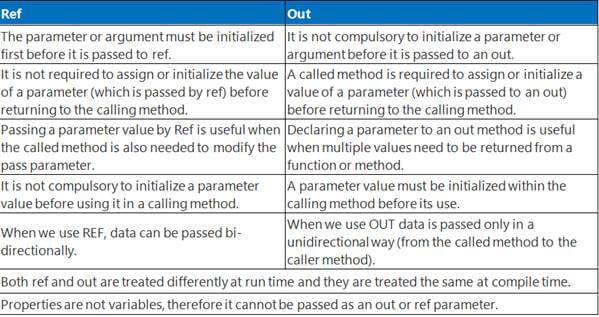
8. What is the difference between ref & out parameters?
An argument passed as ref must be initialized before passing to the method whereas out parameter needs not to be initialized before passing to a method.
The ref keyword passes arguments by reference. It means any changes made to this argument in the method will be reflected in that variable when control returns to the calling method. The out keyword passes arguments by reference. This is very similar to the ref keyword.
class Program
{
static int fmax(int a, int b, ref int min)
{
if (a > b)
{
min = b;
return a;
}
else
{
min = a;
return b;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 5;
int b = 15;
int min=0;
int max = fmax(a, b,ref min);
Console.WriteLine("min value is {0}
and max is {1}",min,max);
}
}9. What is the use of ‘using’ statement in C#?
The ‘using’ block is used to obtain a resource and process it and then automatically dispose of when the execution of the block completed.
10. What is serialization?
When we want to transport an object through a network, then we have to convert the object into a stream of bytes. The process of converting an object into a stream of bytes is called Serialization. For an object to be serializable, it should implement ISerialize Interface. De-serialization is the reverse process of creating an object from a stream of bytes.
11. Can we use “this” command within a static method?
We can’t use ‘This’ in a static method because we can only use static variables/methods in a static method. this keyword is used to refer to the current instance of the class. It is used to access members from the constructors, instance methods, and instance accessors. this keyword is also used to track the instance which is invoked to perform some calculation or further processing related to that instance.
12. What is the difference between constants and read-only?
Constant variables are declared and initialized at compile time. The value can’t be changed afterward. Read-only is used only when we want to assign the value at run time.
13. What is an interface class? Give one example of it
An Interface is an abstract class which has only public abstract methods, and the methods only have the declaration and not the definition. These abstract methods must be implemented in the inherited classes.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoApplication
{
interface Guru99Interface
{
void SetTutorial(int pID, string pName);
String GetTutorial();
}
class Guru99Tutorial : Guru99Interface
{
protected int TutorialID;
protected string TutorialName;
public void SetTutorial(int pID, string pName)
{
TutorialID = pID;
TutorialName = pName;
}
public String GetTutorial()
{
return TutorialName;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Guru99Tutorial pTutor = new Guru99Tutorial();
pTutor.SetTutorial(1,".Net by Guru99");
Console.WriteLine(pTutor.GetTutorial());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
14. What are value types and reference types?
A value type holds a data value within its own memory space. Example
int a = 30;
Reference type stores the address of the Object where the value is being stored. It is a pointer to another memory location.
string b = "Hello Guru99!!";
15. What are Custom Control and User Control?
Custom Controls are controls generated as compiled code (Dlls), those are easier to use and can be added to toolbox. Developers can drag and drop controls to their web forms. Attributes can, at design time. We can easily add custom controls to Multiple Applications (If Shared Dlls). So, If they are private, then we can copy to dll to bin directory of web application and then add reference and can use them.
User Controls are very much similar to ASP include files, and are easy to create. User controls can’t be placed in the toolbox and dragged – dropped from it. They have their design and code-behind. The file extension for user controls is ascx.
16. What are sealed classes in C#?
We create sealed classes when we want to restrict the class to be inherited. Sealed modifier used to prevent derivation from a class. If we forcefully specify a sealed class as base class, then a compile-time error occurs.
17. What is method overloading, Early Binding and Late Binding?
Method overloading is creating multiple methods with the same name with unique signatures in the same class. When we compile, the compiler uses overload resolution to determine the specific method to be invoke.
Early Binding and Late Binding concepts belong to polymorphism in C#. Polymorphism is the feature of object-oriented programming that allows a language to use the same name in different forms. For example, a method named Add can add integers, doubles, and decimals. Polymorphism we have 2 different types to achieve that:
- Compile Time also known as Early Binding or Overloading.
- Run Time is also known as Late Binding or Overriding.
18. What is the difference between Array and Arraylist?
In an array, we can have items of the same type only. The size of the array is fixed when compared. To an arraylist is similar to an array, but it doesn’t have a fixed size.
19. Can a private virtual method can be overridden?
No, because they are not accessible outside the class.
20. Describe the accessibility modifier “protected internal”.
Protected Internal variables/methods are accessible within the same assembly and also from the classes that are derived from this parent class.
21. What are the differences between System.String and System.Text.StringBuilder classes?
System.String is immutable. When we modify the value of a string variable, then a new memory is allocated to the new value and the previous memory allocation released. System.StringBuilder was designed to have a concept of a mutable string where a variety of operations can be performed without allocation separate memory location for the modified string.
22. What’s the difference between the System.Array.CopyTo() and System.Array.Clone() ?
Using Clone() method, we creates a new array object containing all the elements in the original Array and using CopyTo() method. All the elements of existing array copies into another existing array. Both methods perform a shallow copy.
23. How can we sort the elements of the Array in descending order?
Using Sort() methods followed by Reverse() method.
24. Write down the C# syntax to catch an exception
To catch an exception, we use try-catch blocks. Catch block can have a parameter of system.Exception type.
Eg:
try {
GetAllData();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
In the above example, we can omit the parameter from catch statement.
25. What’s the difference between an interface and abstract class?
Interfaces have all the methods having only declaration but no definition. In an abstract class, we can have some concrete methods. In an interface class, all the methods are public. An abstract class may have private methods.
26. What is the difference between Finalize() and Dispose() methods?
Dispose() is called when we want for an object to release any unmanaged resources with them. On the other hand, Finalize() is used for the same purpose, but it doesn’t assure the garbage collection of an object.
27. What are circular references?
A circular reference is a situation in which two or more resources are interdependent on each other causes the lock condition and make the resources unusable. it can create a deadlock situation. The simplest way to avoid deadlock is to use a timeout value.
28. What are generics in C#.NET?
Generics are used to make reusable code classes to decrease the code redundancy, increase type safety, and performance. Using generics, we can create collection classes. To create generic collection, System.Collections.Generic namespace should be used instead of classes such as ArrayList in the System.Collections namespace. Generics promotes the usage of parameterized types.
Collection Classes:
Collection classes are specialized classes for data storage and retrieval. These classes provide support for stacks, queues, lists, and hash tables. Most collection classes implement the same interfaces.
Collection classes serve various purposes, such as allocating memory dynamically to elements and accessing a list of items on the basis of an index, etc. These classes create collections of objects of the Object class, which is the base class for all data types in C#. eg: ArrayList, SortedList, HashTable, Stack, Queue etc.
29. What is an object pool in .NET?
An object pool is a container having objects ready to be used. It tracks the object that is currently in use, total number of objects in the pool. This reduces the overhead of creating and re-creating objects.
30. List down the commonly used types of exceptions in .net
ArgumentException, ArgumentNullException , ArgumentOutOfRangeException, ArithmeticException, DivideByZeroException ,OverflowException , IndexOutOfRangeException ,InvalidCastException ,InvalidOperationException , IOEndOfStreamException , NullReferenceException , OutOfMemoryException , StackOverflowException etc.
31. What are Custom Exceptions?
Sometimes there are some errors that need to be handled as per user requirements. Custom exceptions are used for them and are used defined exceptions.
32. What are delegates?
Delegates are the same as function pointers in C++, but the only difference is that they are type-safe, unlike function pointers. Delegates are required because they can be used to write much more generic type-safe functions.
Learn More about Lambda and Delegates
33. How do you inherit a class into other class in C#?
Colon is used as inheritance operator in C#. Just place a colon and then the class name.
public class DerivedClass : BaseClass
34. What is the base class in .net from which all the classes are derived from?
System.Object
35. What is the difference between method overriding and method overloading?
In method overriding, we change the method definition in the derived class that changes the method behavior. Method overloading is creating a method with the same name within the same class having different signatures.
36. What are the different ways a method can be overloaded?
Methods can be overloaded using different data types for a parameter, different order of parameters, and different number of parameters.
37. Why can’t you specify the accessibility modifier for methods inside the interface?
In an interface, we have virtual methods that do not have method definition. All the methods are there to be overridden in the derived class. That’s why they all are public.
38. How can we set the class to be inherited, but prevent the method from being over-ridden?
Declare the class as public and make the method sealed to prevent it from being overridden.
39. What happens if the inherited interfaces have conflicting method names?
Implement is up to you as the method is inside your own class. There might be a problem when the methods from different interfaces expect different data, but as far as compiler cares you’re okay.
If we implement multiple interfaces in the same class with conflict method names, we don’t need to define all. In other words, we can say if we have conflict methods in the same class, we can’t implement their body independently in the same class because of the same name and same signature. Therefore, we have to use the interface name before the method name to remove this method confiscation. Let’s see an example:
- interface testInterface1 {
- void Show();
- }
- interface testInterface2 {
- void Show();
- }
- class Abc: testInterface1,
- testInterface2 {
- void testInterface1.Show() {
- Console.WriteLine(“For testInterface1 !!”);
- }
- void testInterface2.Show() {
- Console.WriteLine(“For testInterface2 !!”);
- }
- }
Now see how to use these in a class:
- class Program {
- static void Main(string[] args) {
- testInterface1 obj1 = new Abc();
- testInterface1 obj2 = new Abc();
- obj1.Show();
- obj2.Show();
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
Output:
For testInterface1 !!
For testInterface1 !!
40. What is the difference between a Struct and a Class?
Structs are value-type variables, and classes are reference types. Structs stored on the Stack causes additional overhead but faster retrieval. Structs cannot be inherited.
41. How to use nullable types in .Net?
Value types can take either their normal values or a null value. Such types are called nullable types.
Int? someID = null;
If(someID.HasVAlue)
{
}
42. How we can create an array with non-default values?
We can create an array with non-default values using Enumerable.Repeat.
43. What is difference between “is” and “as” operators in c#?
“is” operator is used to check the compatibility of an object with a given type, and it returns the result as Boolean.
“as” operator is used for casting of an object to a type or a class.
44. What’s a multicast delegate?
A delegate having multiple handlers assigned to it is called multicast delegate. Each handler is assigned to a method.
45. What are indexers in C# .NET?
Indexers are known as smart arrays in C#. It allows the instances of a class to be indexed in the same way as an array.
Eg:
public int this[int index] // Indexer declaration
46. What is difference between the “throw” and “throw ex” in .NET?
“Throw” statement preserves original error stack whereas “throw ex” have the stack trace from their throw point. It is always advised to use “throw” because it provides more accurate error information.
47. What are C# attributes and its significance?
C# provides developers a way to define declarative tags on certain entities, eg. Class, method, etc. are called attributes. The attribute’s information can be retrieved at runtime using Reflection.
48. How to implement a singleton design pattern in C#?
In a singleton pattern, a class can only have one instance and provides an access point to it globally.
Eg:
Public sealed class Singleton
{
Private static readonly Singleton _instance = new Singleton();
}
49. What is the difference between directcast and ctype?
DirectCast is used to convert the type of object that requires the run-time type to be the same as the specified type in DirectCast.
Ctype is used for conversion where the conversion is defined between the expression and the type.
50. Is C# code is managed or unmanaged code?
C# is managed code because Common language runtime can compile C# code to Intermediate language.
To put it very simply, managed code is just that: code whose execution is managed by a runtime.
51. What is Console application?
A console application is an application that can be run in the command prompt in Windows. For any beginner on .Net, building a console application is ideally the first step, to begin with.
52. Give an example of removing an element from the queue
The dequeue method is used to remove an element from the queue.
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace DemoApplication
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Queue qt = new Queue();
qt.Enqueue(1);
qt.Enqueue(2);
qt.Enqueue(3);
foreach (Object obj in qt)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("The number of elements in the Queue " + qt.Count);
Console.WriteLine("Does the Queue contain " + qt.Contains(3));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
53. What is Boxing and Unboxing in C#?
Boxing and Unboxing both are used for type conversions. The process of converting from a value type to a reference type is called boxing. Boxing is an implicit conversion. Here is an example of boxing in C#.
// Boxing
- int anum = 123;
- Object obj = anum;
- Console.WriteLine(anum);
- Console.WriteLine(obj);
The process of converting from a reference type to a value type is called unboxing. Here is an example of unboxing in C#.
// Unboxing
- Object obj2 = 123;
- int anum2 = (int)obj;
- Console.WriteLine(anum2);
- Console.WriteLine(obj);
54. What is enum in C#?
An enum is a value type with a set of related named constants often referred to as an enumerator list. The enum keyword is used to declare an enumeration. It is a primitive data type that is user-defined. An enum type can be an integer (float, int, byte, double, etc.). But if you use it beside int it has to be cast. An enum is used to create numeric constants in the .NET framework. All the members of enum are enum type. There must be a numeric value for each enum type. The default underlying type of the enumeration element is int. By default, the first enumerator has the value 0, and the value of each successive enumerator is increased by 1.
enum Dow {Sat, Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri};
Some points about enum,
- Enums are enumerated data types in c#.
- Enums are not for the end-user, they are meant for developers.
- Enums are strongly typed constant. They are strongly typed, i.e. an enum of one type may not be implicitly assigned to an enum of another type even though the underlying value of their members is the same.
- Enumerations (enums) make your code much more readable and understandable.
- Enum values are fixed. Enum can be displayed as a string and processed as an integer.
- The default type is int, and the approved types are byte, sbyte, short, ushort, uint, long, and ulong.
- Every enum type automatically derives from System.Enum and thus we can use System.Enum methods on enums.
- Enums are value types and are created on the stack and not on the heap.
55 What is the difference between “continue” and “break” statements in C#?
Using break statement, you can ‘jump out of a loop’ whereas by using a continue statement, you can ‘jump over one iteration’ and then resume your loop execution
56 What are Properties in C#?
C# properties are members of a C# class that provide a flexible mechanism to read, write or compute the values of private fields, in other words, by using properties, we can access private fields and set their values. Properties in C# are always public data members. C# properties use get and set methods, also known as accessors, to access and assign values to private fields.
What are accessors?
The get and set portions or blocks of a property are called accessors. These are useful to restrict the accessibility of a property. The set accessor specifies that we can assign a value to a private field in a property. Without the set accessor property, it is like a readonly field. With the ‘get’ accessor we can access the value of the private field. In other words, it returns a single value. A Get accessor specifies that we can access the value of a field publically.
We have three types of properties: Read/Write, ReadOnly, and WriteOnly.
57. What is IEnumerable<> in C#?
IEnumerable is the parent interface for all non-generic collections in System.Collections namespace like ArrayList, HastTable etc. that can be enumerated. For the generic version of this interface as IEnumerable<T> which a parent interface of all generic collections class in System.Collections.Generic namespace like List<> and more. In System.Collections.Generic.
IEnumerable<T> have only a single method which is GetEnumerator() that returns an IEnumerator. IEnumerator provides the power to iterate through the collection by exposing a Current property and Move Next and Reset methods if we don’t have this interface as a parent so we can’t use iteration by foreach loop or can’t use that class object in our LINQ query.
58. What are partial classes?
A partial class is only used to split the definition of a class in two or more classes in the same source code file or more than one source file. You can create a class definition in multiple files, but it will be compiled as one class at run time. Also, when you create an instance of this class, you can access all the methods from all source files with the same object. Partial Classes can be created in the same namespace. It isn’t possible to create a partial class in a different namespace. So use the “partial” keyword with all the class names that you want to bind together with the same name of a class in the same namespace.
59. What are extension methods in C#?
Extension methods enable you to add methods to existing types without creating a new derived type, recompiling, or otherwise modifying the original type. An extension method is a special kind of static method, but they are called as if they were instance methods on the extended type.
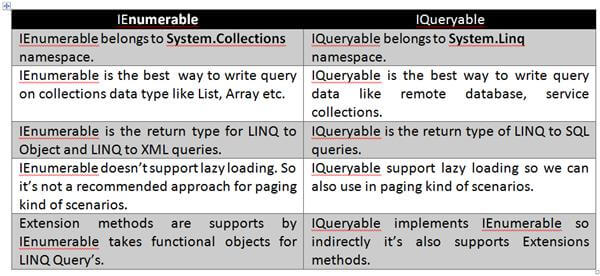
60. What are the differences between IEnumerable and IQueryable?
Before we go into the differences, let’s learn what the IEnumerable and IQueryable are.
IEnumerable Is the parent interface for all non-generic collections in System.Collections namespace like ArrayList, HastTable, etc. that can be enumerated. The generic version of this interface is IEnumerable<T>, which a parent interface of all generic collections class in System.Collections.Generic namespace, like List<> and more.
IQueryable As per MSDN, the IQueryable interface is intended for implementation by query providers. It is only supposed to be implemented by providers that also implement IQueryable<T>. If the provider does not also implement IQueryable<T>, the standard query operators cannot be used on the provider’s data source. The IQueryable interface inherits the IEnumerable interface so that if it represents a query, the results of that query can be enumerated. Enumeration causes the expression tree associated with an IQueryable object to be executed. The definition of “executing an expression tree” is specific to a query provider. For example, it may involve translating the expression tree to an appropriate query language for the underlying data source. Queries that do not return enumerable results are executed when the Execute method is called.
61. What is a dynamic array?
C# supports both static and dynamic arrays. If you’re new to arrays, check out Working With Arrays in C#. A static array has a fixed size and defined when an array is declared. The following code defines an array that can hold 5 int type data only.
- int[] odds = new int[5];
Arrays in C# are 0th index. That means the first item of an array starts at the 0th position. The position of the last item on an array will total number of items – 1. So, if an array has 5 items, the last item of the array is access by using index 4. The following code adds 5 items to the array.
- odds[0] = 1;
- odds[1] = 3;
- odds[2] = 5;
- odds[3] = 7;
- odds[4] = 9;
In a fixed array, if you try to add more items than its range, you will get the following error:
- odds[5] = 11;
Unhandled exception. System.IndexOutOfRangeException: Index was outside the bounds of the array. at Program.Main(String[] args) in C:\Mahesh\DotNetCore\ArraysFAQ\ArraysFAQ\Program.cs:line 14 A dynamic array does not have a predefined size. The size of a dynamic array increases as you add new items to the array. You can declare an array of fixed length or dynamic. You can even change a dynamic array to static after it is defined. The following code snippet declares a dynamic array where the size of the array is not provided.
int[] numArray = new int[] {};
Dynamic arrays can be initialized as static arrays. The following code snippet declares a dynamic array and initializes.
int[] numArray = new int[] { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 };
62. What is the Constructor Chaining in C#?
Constructor chaining is a way to connect two or more classes in a relationship as Inheritance. In Constructor Chaining, every child class constructor is mapped to a parent class Constructor implicitly by base keyword, so when you create an instance of the child class, it will call the parent’s class Constructor. Without it, inheritance is not possible.
63. Difference between the Equality Operator (==) and Equals() Method in C#
Both the == Operator and the Equals() method are used to compare two value type data items or reference type data items. The Equality Operator (==) is the comparison operator and the Equals() method compares the contents of a string. The == Operator compares the reference identity while the Equals() method compares only contents.
64. What is a Virtual Method in C#?
A virtual method is a method that can be redefined in derived classes. A virtual method has an implementation in a base class as well as derived the class. It is used when a method’s basic functionality is the same but sometimes more functionality is needed in the derived class. A virtual method is created in the base class that can be overridden in the derived class. We create a virtual method in the base class using the virtual keyword and that method is overridden in the derived class using the override keyword. When a method is declared as a virtual method in a base class then that method can be defined in a base class and it is optional for the derived class to override that method. The overriding method also provides more than one form for a method. Hence, it is also an example of polymorphism. When a method is declared as a virtual method in a base class and that method has the same definition in a derived class then there is no need to override it in the derived class. But when a virtual method has a different definition in the base class and the derived class then there is a need to override it in the derived class. When a virtual method is invoked, the run-time type of the object is checked for an overriding member. The overriding member in the most derived class is called, which might be the original member if no derived class has overridden the member.
Virtual Method
- By default, methods are non-virtual. We can’t override a non-virtual method.
- We can’t use the virtual modifier with static, abstract, private or override modifiers.
65. What are Anonymous Types in C#?
Anonymous types allow us to create new types without defining them. This is a way of defining read-only properties in a single object without having to define each type explicitly. Here, Type is generated by the compiler and is accessible only for the current block of code. The type of properties is also inferred by the compiler. We can create anonymous types by using “new” keyword together with the object initializer.
Example
- var anonymousData = new
- {
- ForeName = “Jignesh”,
- SurName = “Trivedi”
- };
- Console.WriteLine(“First Name : ” + anonymousData.ForeName);
Anonymous Types with LINQ
Anonymous types are also used with the “Select” clause of LINQ query expression to return a subset of properties.
66. What is a Hashtable in C#?
A Hashtable is a collection that stores (Keys, Values) pairs. Here, the Keys are used to find the storage location and is immutable and cannot have duplicate entries in a Hashtable. The .Net Framework has provided a Hash Table class that contains all the functionality required to implement a hash table without any additional development. The hash table is a general-purpose dictionary collection. Each item within the collection is a DictionaryEntry object with two properties: a key object and a value object. These are known as Key/Value. When items are added to a hash table, a hash code is generated automatically. This code is hidden from the developer. Access to the table’s values is achieved using the key object for identification. As the items in the collection are sorted according to the hidden hash code, the items should be considered to be randomly ordered. The Hashtable Collection The Base Class libraries offer a Hashtable Class that is defined in the System.Collections namespace, so you don’t have to code your own hash tables. It processes each key of the hash that you add every time and then uses the hash code to look up the element very quickly. The capacity of a hash table is the number of elements the hash table can hold. As elements are added to a hash table, the capacity is automatically increased as required through reallocation. It is an older .Net Framework type. Declaring a Hashtable The Hashtable class is generally found in the namespace called System.Collections. So to execute any of the examples, we have to add using System.Collections; to the source code. The declaration for the Hashtable is:
- Hashtable HT = new Hashtable ();
67. What is LINQ in C#?
LINQ stands for Language Integrated Query. LINQ is a data querying methodology that provides querying capabilities to .NET languages with a syntax similar to a SQL query. LINQ has a great power of querying on any source of data. The data source could be collections of objects, database or XML files. We can easily retrieve data from any object that implements the IEnumerable<T> interface.
Advantages of LINQ
- LINQ offers an object-based, language-integrated way to query over data no matter where that data came from. So through LINQ, we can query a database and XML as well as collections.
- Compile-time syntax checking.
It allows you to query collections like arrays, enumerable classes, etc… in the native language of your application, like in VB or C# in much the same way you would query a database using SQL.
68. What is File Handling in C#.Net?
The System.IO namespace provides four classes that allow you to manipulate individual files, as well as interact with a machine directory structure. The Directory and File directly extend System.Object and supports the creation, copying, moving and deletion of files using various static methods. They only contain static methods and are never instantiated. The FileInfo and DirecotryInfo types are derived from the abstract class FileSystemInfo type and they are typically employed for obtaining the full details of a file or directory because their members tend to return strongly typed objects. They implement roughly the same public methods as a Directory and a File but they are stateful and members of these classes are not static.
69. What is Reflection in C#?
Reflection is the process of runtime type discovery to inspect metadata, CIL code, late binding, and self-generating code. At the run time by using reflection, we can access the same “type” information as displayed by the ildasm utility at design time. The reflection is analogous to reverse engineering in which we can break an existing *.exe or *.dll assembly to explore defined significant contents information, including methods, fields, events, and properties. You can dynamically discover the set of interfaces supported by a given type using the System.Reflection namespace. Reflection typically is used to dump out the loaded assemblies list, their reference to inspect methods, properties etcetera. Reflection is also used in the external disassembling tools such as Reflector, Fxcop, and NUnit because .NET tools don’t need to parse the source code similar to C++. Metadata Investigation The following program depicts the process of reflection by creating a console-based application. This program will display the details of the fields, methods, properties, and interfaces for any type within the mscorlib.dll assembly. Before proceeding, it is mandatory to import “System.Reflection”. Here, we are defining a number of static methods in the program class to enumerate fields, methods, and interfaces in the specified type. The static method takes a single “System.Type” parameter and returns void.
- static void FieldInvestigation(Type t) {
- Console.WriteLine(“*********Fields*********”);
- FieldInfo[] fld = t.GetFields();
- foreach(FieldInfo f in fld) {
- Console.WriteLine(“–>{0}”, f.Name);
- }
- }
- static void MethodInvestigation(Type t) {
- Console.WriteLine(“*********Methods*********”);
- MethodInfo[] mth = t.GetMethods();
- foreach(MethodInfo m in mth) {
- Console.WriteLine(“–>{0}”, m.Name);
- }
- }
Needs More clarity on the difference between directcast and ctype.